Using BGP peer-groups on Cisco routers
BGP `peer-groups` consolidate common configuration items to a single statement. Eliminating the need to unnecessarily duplicate configuration on each neighbor.
608 Words
2021-03-04 06:02 -0600
Overview
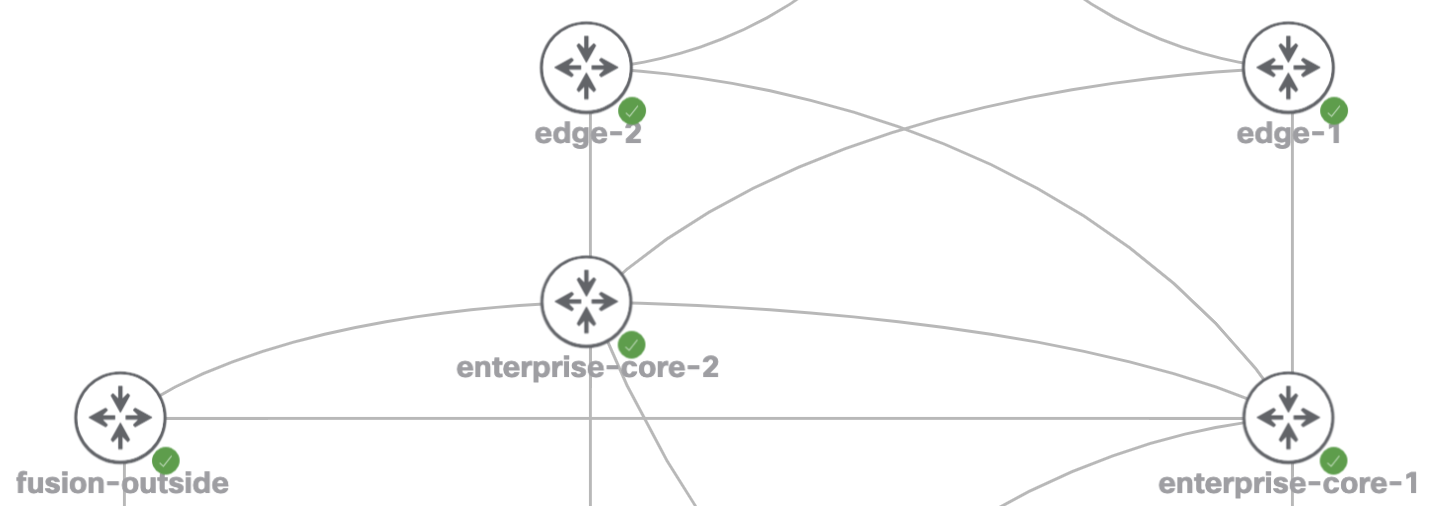
BGP peer-groups consolidate common configuration items to a single statement. Eliminating the need to unnecessarily duplicate configuration on each neighbor. In the example topology below, there are 4 ibgp neighbors per router, each replicating the same two lines. By using peer-groups we eliminate 4 lines from the bgp configuration. In addition, if new lines or updates are required, a single change will update all neighbors.
ibgp full mesh between all routers:
Details
Example configuration from the edge-2 router. By using the ibgp_group_65000 peer-group, we eliminate multiple lines of duplicated configuration and allow for streamlined changes in the future:
router bgp 65000
bgp router-id interface Loopback0
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor ibgp_group_65000 peer-group
neighbor ibgp_group_65000 remote-as 65000
neighbor ibgp_group_65000 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 192.168.0.1 remote-as 65200
neighbor 192.168.200.1 peer-group ibgp_group_65000
neighbor 192.168.200.3 peer-group ibgp_group_65000
neighbor 192.168.200.4 peer-group ibgp_group_65000
neighbor 192.168.200.10 peer-group ibgp_group_65000
!
address-family ipv4
network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
neighbor 192.168.0.1 activate
neighbor 192.168.200.1 activate
neighbor 192.168.200.3 activate
neighbor 192.168.200.4 activate
neighbor 192.168.200.10 activate
exit-address-family
Quickly view all routers within a peer-group:
edge-2#show ip bgp peer-group ibgp_group_65000
BGP peer-group is ibgp_group_65000, remote AS 65000
BGP version 4
Neighbor sessions:
0 active, is not multisession capable (disabled)
Do log neighbor state changes (via global configuration)
Default minimum time between advertisement runs is 0 seconds
For address family: IPv4 Unicast
BGP neighbor is ibgp_group_65000, peer-group internal, members:
192.168.200.1 192.168.200.3 192.168.200.4 192.168.200.10
Index 0, Advertise bit 0
Update messages formatted 0, replicated 0
Number of NLRIs in the update sent: max 0, min 0
Validate ibgp peer-group sessions are established and exchanging routes:
edge-2#show ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 192.168.200.2, local AS number 65000
BGP table version is 6, main routing table version 6
3 network entries using 744 bytes of memory
5 path entries using 720 bytes of memory
4/3 BGP path/bestpath attribute entries using 1152 bytes of memory
1 BGP AS-PATH entries using 24 bytes of memory
0 BGP route-map cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
0 BGP filter-list cache entries using 0 bytes of memory
BGP using 2640 total bytes of memory
BGP activity 3/0 prefixes, 5/0 paths, scan interval 60 secs
3 networks peaked at 01:26:01 Mar 4 2021 UTC (00:41:53.359 ago)
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
192.168.0.1 4 65200 53 52 6 0 0 00:43:38 2
192.168.200.1 4 65000 25 26 6 0 0 00:17:59 2
192.168.200.3 4 65000 13 18 6 0 0 00:09:16 0
192.168.200.4 4 65000 16 20 6 0 0 00:11:47 0
192.168.200.10 4 65000 11 16 6 0 0 00:07:56 0
Validate routes are propagated between routers:
enterprise-core-2#show ip route bgp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, m - OMP
n - NAT, Ni - NAT inside, No - NAT outside, Nd - NAT DIA
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
H - NHRP, G - NHRP registered, g - NHRP registration summary
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is 192.168.0.3 to network 0.0.0.0
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [200/0] via 192.168.0.3, 00:09:14
B 172.16.0.0/12 [200/0] via 192.168.0.3, 00:09:14
B 192.168.0.0/16 [200/0] via 192.168.200.2, 00:09:14